
To begin the process, pick one of these display options.

What data to display: content, users, comments, and moreĪs you go to Structure > Views > Add view on your Drupal administration dashboard, you need to give your view a name and optionally write a description that only you and other admins will see. We will share helpful directions so this section can also be used as a step-by-step guide to using Drupal Views. We will now show you the most important Views concepts in the order they are often applied.
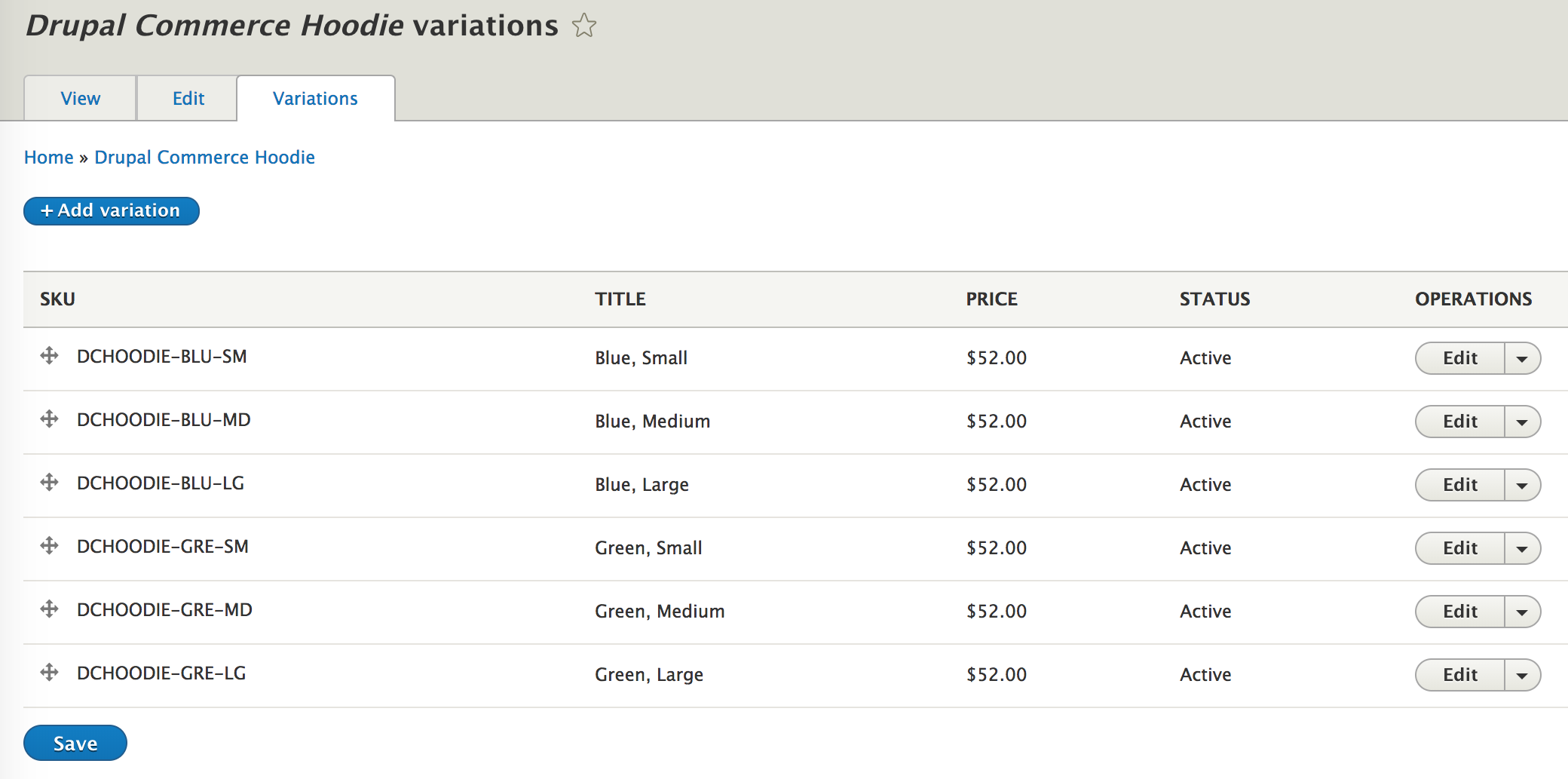
DRUPAL COMMERCE IMAGE DISPLAY HOW TO
How to work with Drupal Views: key concepts and settings Let’s move on to reviewing at least the most standard ones. The content listing capabilities of Views are really unlimited, with even the most complex scenarios possible. Ideally, it should be a site builder or a developer. It’s preferable that it is handled by a tech-savvy person with a good understanding of Drupal structure and concepts. In Drupal 7 where Views are not included in the core, this module remains the 2nd most popular contributed module among 40,000+ others.ĭespite its content listing mission, the tool is not exactly meant for every content editor to play with. Additionally, standard administration tools are built with Views, allowing for site builders to modify their functionality without touching any code. Moreover no individual updates are required for the modules. Having Views as part of the Drupal core is incredibly convenient because everything is available out of the box, there is nothing to install. The Views UI module provides you with the interface for creating and editing your content listings. The Views module is the “engine” of data handling. But they became part of the Drupal core with the release of Drupal 8 in 2015. Views, together with its assistant Views UI (the Views builder user interface), are Drupal modules that were previously contributed modules. In this way, you can display a page with your latest articles, create an image slideshow, build an interactive map, show a block with related content, and so much more. The tool makes a query to your website’s database to fetch the necessary data and displays it according to the criteria you specify. Views are built via a handy interface by choosing which data you want to display on your website, and how. Users, comments, taxonomies, and other Drupal entities can also be incorporated into an organized collection. Views are a solution for creating content listings, or rather, data listings because their use is not limited to content. Also we'll suggest some interesting extra modules that expand their powers even further. We will overview their key capabilities, add some helpful step-by-step guides on how to use Views in Drupal. Today, Drupal Views will be the main hero of our blog post. It's the ability to organize content in flexible ways via the user interface with no need to write complex SQL queries.

This powerful tool brings out the best in the philosophy of a content management system. The overwhelming majority of Drupal websites are using Views for content collections. When you come across an organized content listing on any Drupal website, you can bet it’s built with Views.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
